svn switch --relocate [old_location] [new_location]Monday, November 24, 2008
How to relocate an SVN location
To switch the svn location which you were working, to a new location you can use the following command
Monday, November 10, 2008
How to invoke a Proxy Service created on WSO2 ESB deployed on IBM Websphere
When you deploy WSO2 ESB on IBM Webphere you will not be able to invoke the created Proxy services or sequences the general way you do it. This requires a new parameter to be given and the ports too should be correctly specified.
Assume that the web context root given when deploying WSO2 ESB is 'esb'. Also if the specified HTTP port of IBM Websphere is 9080, you can invoke a Proxy service which you have created on WSO2 ESB as follows.
Assume that the web context root given when deploying WSO2 ESB is 'esb'. Also if the specified HTTP port of IBM Websphere is 9080, you can invoke a Proxy service which you have created on WSO2 ESB as follows.
ant stockquote -Dtrpurl=http://localhost:<HTTPS_port_of_WAS>/
<web_context_root>/soap/<Proxy_name>
E.g.:- ant stockquote -Dtrpurl=http://localhost:9080/esb/soap/SimpleProxy
Tuesday, November 4, 2008
Performance testing on a Derby database - JMeter to the rescue
One of my friends had a requirement of doing a performance test on a Derby database and she proposed that it would be easier if we do it through Apache JMeter. This was quite new to me and had to do a lot of Google searches but at the end was able to get it working so thought of sharing it with you all. I assume that you all are familiar with Apache JMeter. I will simply explain the steps along with some screen shots.
Step 1
Download and install Apache JMeter on your local machine and start the jmeter.bat file which is located inside the bin folder. Once you start the bat file you it will open up Apache JMeter as shown on the Figure.
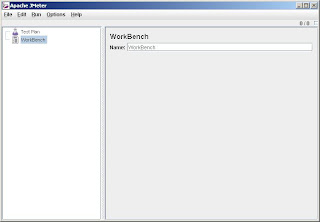
Step 2
Now let us add the things which are required to do our task.
First right click on the 'Test Plan' element and add a Thread Group.
The next thing you need to add is a JDBC configuration element. To do this right click on the 'Thread Group' which you added a while ago and select 'Add -> Config Element -> JDBC Connection Configuration'.
Now you need to fill up the information to depending on the database which you have selected. Let us see what values we need to enter to test a Derby database. The following screen shot will give you a clear idea on this.
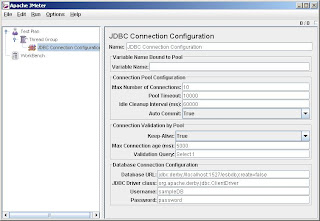
Step 3
The next step is to add a 'JDBC Request' element to enter you database query. Assume that you have created a database on your Derby database and that you have a table called 'COMPANY'. Let us see how you can query this database.
Right click on the 'Thread Group' and select 'Add -> Sampler -> JDBC Request'.
Since we are going to do select some data from the database, select the the option 'Select Statement' from the combo box 'Query Type:'.
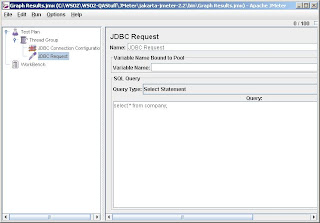
Step 4
Now you need to find a way to view the performance. In order to do this you can add a listener to view the results. Therefore right click on the 'Thread Group' and select 'Add -> Listener -> Graph Results'
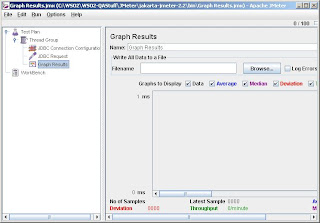
Step 5
Before running the test w need one more step to follow. That is to specify the number of threads. To do this click on the 'Thread Group' and specify 1000 as 'Number of Threads (users):' which is under 'Thread Properties'.
Let us try this out now. From the main menu select 'Run -> Start'. If you are executing the test for the first time it would ask you to save the test plan. Save the test plan at any location you prefer. Once the test has executed, you will see the output as shown in the following graph. You can do your test as you prefer by changing the number of threads.

Step 1
Download and install Apache JMeter on your local machine and start the jmeter.bat file which is located inside the bin folder. Once you start the bat file you it will open up Apache JMeter as shown on the Figure.

Step 2
Now let us add the things which are required to do our task.
First right click on the 'Test Plan' element and add a Thread Group.
The next thing you need to add is a JDBC configuration element. To do this right click on the 'Thread Group' which you added a while ago and select 'Add -> Config Element -> JDBC Connection Configuration'.
Now you need to fill up the information to depending on the database which you have selected. Let us see what values we need to enter to test a Derby database. The following screen shot will give you a clear idea on this.

Step 3
The next step is to add a 'JDBC Request' element to enter you database query. Assume that you have created a database on your Derby database and that you have a table called 'COMPANY'. Let us see how you can query this database.
Right click on the 'Thread Group' and select 'Add -> Sampler -> JDBC Request'.
Since we are going to do select some data from the database, select the the option 'Select Statement' from the combo box 'Query Type:'.

Step 4
Now you need to find a way to view the performance. In order to do this you can add a listener to view the results. Therefore right click on the 'Thread Group' and select 'Add -> Listener -> Graph Results'

Step 5
Before running the test w need one more step to follow. That is to specify the number of threads. To do this click on the 'Thread Group' and specify 1000 as 'Number of Threads (users):' which is under 'Thread Properties'.
Let us try this out now. From the main menu select 'Run -> Start'. If you are executing the test for the first time it would ask you to save the test plan. Save the test plan at any location you prefer. Once the test has executed, you will see the output as shown in the following graph. You can do your test as you prefer by changing the number of threads.

Sunday, October 26, 2008
Developing a Research Thesis
The third semester is about to end of my MBA and it's time to spend some time on the MBA research. Selecting a research topic is difficult. Doing literature review and developing on the thesis is even harder. After a chat which I had with Dr. Sanjiva Weerawarana I decided that I should select a topic which would be useful for WSO2, my organization that I work for as well and therefore thought of touching the area of marketing open-source software. I have no clue on where to start and at the moment am browsing through the web and collecting related magazines, articles which I think might be useful for me.
I wish my father was alive because I'm sure I would have had great support from him since he has done similar kinds of stuff and helped a lot of other people who have done their research projects. He did his PhD on radiochemistry and his research paper is available on the web but unfortunately I cannot access is since I have to pay in order to download it.
I could have got some help from my dear old sister who is a medical doctor at the University of Ragama but alas she too is doing her PhD these days and I don't think I will get any help from her either (She too has written some articles on her research).
So I guess I'm alone on this and will have to do it on my own. Well of course we are expected to do it on our own but it would have been great if I had someone who's close to me who would at least would understand my stress at a time like this. I know that there will be a lot of people at office to help me out but it won't be the same. We will see how it goes. My only hope is to be able to complete it by 2009 and graduate with the rest of the batch. :-)
I wish my father was alive because I'm sure I would have had great support from him since he has done similar kinds of stuff and helped a lot of other people who have done their research projects. He did his PhD on radiochemistry and his research paper is available on the web but unfortunately I cannot access is since I have to pay in order to download it.
I could have got some help from my dear old sister who is a medical doctor at the University of Ragama but alas she too is doing her PhD these days and I don't think I will get any help from her either (She too has written some articles on her research).
So I guess I'm alone on this and will have to do it on my own. Well of course we are expected to do it on our own but it would have been great if I had someone who's close to me who would at least would understand my stress at a time like this. I know that there will be a lot of people at office to help me out but it won't be the same. We will see how it goes. My only hope is to be able to complete it by 2009 and graduate with the rest of the batch. :-)
Friday, October 24, 2008
Creating your own Web Service with different session scopes
When creating a Web service you can create Web services of different session scopes. There are four session types in Axis2 such as,
1. SOAP Session Scope
2. Transport Session Scope
3. Request Scope
4. Application Session Scope
I will briefly explain how one can create Web service with each of these different session scopes.
Once you have created your Java class and complied it, you will need to write a services.xml before converting it into an archive file.
In order to create a service with a SOAP session scope all you have to do is add the following to your services.xml
scope="soapsession"
I will be providing a sample service.xml for your reference.
1. SOAP Session Scope
2. Transport Session Scope
3. Request Scope
4. Application Session Scope
I will briefly explain how one can create Web service with each of these different session scopes.
Once you have created your Java class and complied it, you will need to write a services.xml before converting it into an archive file.
In order to create a service with a SOAP session scope all you have to do is add the following to your services.xml
scope="soapsession"
E.g.:- <service name="<service_name>" scope="soapsession">
I will be providing a sample service.xml for your reference.
<service name="Adding" scope="soapsession">
<description>
This service is created to add two numbers.
</description>
<parameter name="ServiceClass" locked="false">com.math.add.Adding</parameter>
<operation name="add">
<messageReceiver class="org.apache.axis2.rpc.receivers.RPCMessageReceiver"/>
</operation>
</service>
Tuesday, October 21, 2008
Creating your own 'Mediator'
Recently I was asked by Ruwan to verify an issue reported by some customer. In order to test the issue, I had to write a new mediator. Since I'm not much familiar with writing these sort of stuff, I was struggling hard to get it working and in the end Ruwan helped me out to write a simple mediator and also taught me how to test it with WSO2 ESB. I will briefly describe how this can be done easily.
Pre-requisites - You need to download and install the latest version of WSO2 ESB on your local machine. (Assume that you have downloaded the WSO2 ESB instance to C:\wso2esb-1.7. I will be referring to this folder as ESB_HOME from this point onwards)
Step 1 - Create a mediator class
As the initial step I wrote a small java class which extends the method AbstractMediator as below.
Assume that you have your compiled java class at C:\ESB\mediator\testMediator\org\wso2\esb\client\TestMediator.class
Step 2 - Creating the JAR file
After compiling the class, I created a JAR file using the compiled class.
Open a new command prompt and go to the folder which you have the compiled package (E.g.:- C:\ESB\mediator\testMediator) and type the following command
Once you type this command it would create the JAR file testMediator.jar at the current location (E.g.:- C:\ESB\mediator\testMediator )
Step 3 - Creating the synapse configuration
In order to test the newly created mediator you can use a simple configuration as below. You can call the mediator which you created using a class mediator ( E.g.:- <class name="org.wso2.esb.client.TestMediator"/> ).
Step 4 - Starting the WSO2 ESB server with the created configuration
Copy this configuration to the ESB_HOME\webapp\WEB-INF\classes\conf and start the WSO2 ESB server. To do this, go to ESB_HOME\bin and run the command wso2-esb.bat
Step 5 - Creating the client to invoke the service
Assume that you have created a service (For you reference I will be attaching the service Adding1.aar which I have created) and deploy it in ESB_HOME\samples\axis2Server\repository\services. Go to the folder ESB_HOME\samples\axis2Server and start the SimpleAxis2Server by executing the executable bat file 'axis2server.bat'.
Now create a client as below and invoke the service deployed through WSO2 ESB.
Step 6 - Verifying through viewing the logs
Once you invoke the client, the logs displayed on the WSO2 ESB console will show how the class mediator has been invoked
As you can see only the Class mediator is invoked and non of the mediators specified after wards are not invoked. The reason for this is that when creating the mediator, you have set 'return' to false. Therefore when the Class mediator is invoked none of the mediators available after that Class mediator will not be invoked. If you need to invoke the other mediators that are available after the Class mediator, you have to set 'return' to true. Try this out by yourself. Once you execute the client, it should invoke the Class mediator first and the the Log mediator and after that the rest of the mediators specified.
Pre-requisites - You need to download and install the latest version of WSO2 ESB on your local machine. (Assume that you have downloaded the WSO2 ESB instance to C:\wso2esb-1.7. I will be referring to this folder as ESB_HOME from this point onwards)
Step 1 - Create a mediator class
As the initial step I wrote a small java class which extends the method AbstractMediator as below.
package org.wso2.esb.client;
import org.apache.axiom.soap.SOAPFault;
import org.apache.synapse.MessageContext;
import org.apache.synapse.mediators.AbstractMediator;
public class TestMediator extends AbstractMediator{
public boolean mediate(MessageContext synCtx) {
SOAPFault fault = synCtx.getEnvelope().getBody().getFault();
System.out.println(fault.getCode().getText());
System.out.println(fault.getReason().getText());
return false;
}
}
Assume that you have your compiled java class at C:\ESB\mediator\testMediator\org\wso2\esb\client\TestMediator.class
Step 2 - Creating the JAR file
After compiling the class, I created a JAR file using the compiled class.
Open a new command prompt and go to the folder which you have the compiled package (E.g.:- C:\ESB\mediator\testMediator) and type the following command
jar cf testMediator.jar org
Once you type this command it would create the JAR file testMediator.jar at the current location (E.g.:- C:\ESB\mediator\testMediator )
Step 3 - Creating the synapse configuration
In order to test the newly created mediator you can use a simple configuration as below. You can call the mediator which you created using a class mediator ( E.g.:- <class name="org.wso2.esb.client.TestMediator"/> ).
<definitions xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse">
<registry provider="org.wso2.esb.registry.ESBRegistry">
<parameter name="root">file:registry/</parameter>
<parameter name="cachableDuration">15000</parameter>
</registry>
<sequence name="main">
<sequence key="sampleSequence"/>
</sequence>
<sequence name="fault">
<log level="full">
<property name="MESSAGE" value="Executing default "fault" sequence"/>
<property name="ERROR_CODE" expression="get-property('ERROR_CODE')"/>
<property name="ERROR_MESSAGE" expression="get-property('ERROR_MESSAGE')"/>
</log>
<drop/>
</sequence>
<sequence name="sampleSequence" onError="soap11_fault">
<in>
<send>
<endpoint>
<address format="soap11" uri="http://localhost:9000/soap/Adding1"/>
</endpoint>
</send>
</in>
<out>
<class name="org.wso2.esb.client.TestMediator"/>
<log level="full"/>
<class name="org.wso2.esb.client.TestMediator"/>
<send/>
</out>
</sequence>
<sequence name="soap11_fault">
<log level="full" separator=","/>
<makefault version="soap11">
<code xmlns:sf11="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/encoding/" value="sf11:VersionMismatch"/>
<reason value="Exception occurred when transforming the request/response"/>
</makefault>
<log level="full"/>
<header name="To" action="remove"/>
<property name="RESPONSE" value="true"/>
</sequence>
</definitions>
Step 4 - Starting the WSO2 ESB server with the created configuration
Copy this configuration to the ESB_HOME\webapp\WEB-INF\classes\conf and start the WSO2 ESB server. To do this, go to ESB_HOME\bin and run the command wso2-esb.bat
Step 5 - Creating the client to invoke the service
Assume that you have created a service (For you reference I will be attaching the service Adding1.aar which I have created) and deploy it in ESB_HOME\samples\axis2Server\repository\services. Go to the folder ESB_HOME\samples\axis2Server and start the SimpleAxis2Server by executing the executable bat file 'axis2server.bat'.
Now create a client as below and invoke the service deployed through WSO2 ESB.
package org.wso2.esb.client;
import org.apache.axiom.om.OMAbstractFactory;
import org.apache.axiom.om.OMElement;
import org.apache.axiom.om.OMFactory;
import org.apache.axiom.om.OMNamespace;
import org.apache.axis2.AxisFault;
import org.apache.axis2.addressing.EndpointReference;
import org.apache.axis2.client.Options;
import org.apache.axis2.client.ServiceClient;
public class AxiomClient {
public static void main(String[] args)throws AxisFault{
Options options = new Options();
options.setTo(new EndpointReference("http://localhost:8280/soap"));
options.setAction("urn:add");
ServiceClient sender = new ServiceClient();
sender.setOptions(options);
OMElement result = sender.sendReceive(getPayload());
System.out.println(result);
}
private static OMElement getPayload() {
OMFactory fac = OMAbstractFactory.getOMFactory();
OMNamespace omNs = fac.createOMNamespace("http://service.esb.wso2.org", "ns");
OMElement method = fac.createOMElement("add", omNs);
OMElement value1 = fac.createOMElement("x", omNs);
OMElement value2 = fac.createOMElement("y", omNs);
value1.addChild(fac.createOMText(value1, "10"));
value2.addChild(fac.createOMText(value2, "10"));
method.addChild(value1);
method.addChild(value2);
return method;
}
}
Step 6 - Verifying through viewing the logs
Once you invoke the client, the logs displayed on the WSO2 ESB console will show how the class mediator has been invoked
[HttpClientWorker-1] DEBUG InMediator Start : In mediator
[HttpClientWorker-1] DEBUG InMediator Current message is a response - skipping child mediators
[HttpClientWorker-1] DEBUG InMediator End : In mediator
[HttpClientWorker-1] DEBUG OutMediator Start : Out mediator
[HttpClientWorker-1] DEBUG OutMediator Current message is outgoing - executing child mediators
[HttpClientWorker-1] DEBUG OutMediator Sequence <OutMediator> :: mediate()
[HttpClientWorker-1] DEBUG ClassMediator Start : Class mediator
[HttpClientWorker-1] DEBUG ClassMediator invoking : class org.wso2.esb.client.TestMediator.mediate()
axis2ns8:Client
The service cannot be found for the endpoint reference (EPR) http://localhost:9000/soap/Adding1
[HttpClientWorker-1] DEBUG ClassMediator End : Class mediator
[HttpClientWorker-1] DEBUG OutMediator End : Out mediator
As you can see only the Class mediator is invoked and non of the mediators specified after wards are not invoked. The reason for this is that when creating the mediator, you have set 'return' to false. Therefore when the Class mediator is invoked none of the mediators available after that Class mediator will not be invoked. If you need to invoke the other mediators that are available after the Class mediator, you have to set 'return' to true. Try this out by yourself. Once you execute the client, it should invoke the Class mediator first and the the Log mediator and after that the rest of the mediators specified.
Tuesday, October 7, 2008
Deploying WSO2 ESB on an IBM WebSphere Application Server
Applies To
1. WSO2 Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) Version 1.7
2. WebSphere Application Server Version 6.1
Download the WebSphere Application Server Version 6.1 and execute the setup to install it on your local machine.
Before deploying the WSO2 ESB application we need to create a profile through the Profile Management Tool. This is described in detail in the tutorial Running WSO2 WSAS on an IBM WebSphere Application Server under the heading Creating an IBM WebSphere Application Server Profile by Upul Godage.
NOTE: Make sure you set the HTTPS transport port to 9444.
Once you have created the profile start the application server through Start -> All Programs -> IBM WebSphere -> Application Server V6.1 -> Profiles -> [your_profile] -> Start the server.
When the server is started successfully access the Administrative Console through Start -> All Programs -> IBM WebSphere -> Application Server V6.1 -> Profiles -> [your_profile] -> Administrative Console.
Once clicked it would open up a web browser. Enter the username and password that we gave in the Administrative Security step when creating the profile and then click on the button Log in.
Download WSO2 ESB version 1.7 from the WSO2 site and extract it to a preferred location of yours. (E.g.:- C:\wso2esb-1.7.1). From this point onwards I will be referring to this folder as ESB_HOME. Before creating the war file you need to change some of the configuration files. Let us look at these files one by one.
1. axis2.xml
a) Open the axis2.xml located at ESB_HOME/webapp/WEB-INF/classes/conf
b) Search all the places where it specifies the jks file locations and replace them with the absolute paths.
2. web.xml
a) Open the web.xml file located at ESB_HOME/webapp/WEB-INF
b) Specify the absolute location of the ESB_HOME
Next we have to start up a Derby server for WSO2 ESB to connect to. Since we have an issue in getting the Derby server which resides in Websphere up and running, we will be starting an external Derby server.
To do this, download the latest Derby binary and extract to a preferred location of yours. For testing purposes we will be using version 10.3.1.4. Then go to the folder DERBY_HOME/bin folder and type the following command.
To direct the WSO2 ESB to connect to the external Derby server you need to set the StartEmbeddedDerby property to 'false' of the ESB_HOME/webapp/WEB-INF/classes/conf/server.xml file
You are all set to create the war file. Now go to the folder 'webapp' of your ESB_HOME and open a command window.
Type the following command and it will create esb.war file in ESB_HOME/webapp folder
Follow the step described below to successfully install the WSO2 ESB application.
1. Once logged in to the Administrative Console, click on Applications -> Install New Application
2. Under Preparing for the application installation browse for the esb.war file that you created above. Specify the context root as esb. If you need to see the steps when installing the WSO2 ESB Application, select the combo box option Show me all installation options and parameters and click Next.
3. From the page loaded to generate default bindings and mappings click on Next without changing any options
4. Click on Continue given under Application Security Warnings page
5. When Install New Application -> Select installation options is loaded specify a name that you prefer as the Application name. Tick the check box Enable class reloading and specify the Reload interval in seconds as 60 seconds and then click on Next
6. Under Install New Application -> Map modules to servers do not select any options and just click on the button Next
7. When the page Install New Application -> Provide JSP reloading options for Web modules loads click on the button Next without selecting anything
8. Next do not select any options given under the page Install New Application -> Map shared libraries and simply click on Next
9. When the page Install New Application -> Initialize parameters for servlets is loaded check whether the specified parameters are correct and click on Next
10. Click on Next without selecting any options when Install New Application -> Map virtual hosts for Web modules page is loaded
11. Verify whether the value given as the context root is correct in the page Install New Application -> Map context roots for Web modules and click on Next
12. When the Install New Application -> Summary page loads, go through the values which you have specified and if they are correct click on Finish
Once you click on Continue you will get a message as follows. Therefore click on Save and the application will be installed successfully.
Go to Applications -> Enterprise Applications and click on the esb entry from the list of applications available.
Then refer the section Configuring IBM WebSphere Application Server in the tutorial Running WSO2 WSAS on an IBM WebSphere Application Server by Upul Godage.
Follow the steps specified and once you are done with setting all the properties select the esb application from the Enterprise Applications list and click on Start. This will start the WSO2 ESB server. If the server starts successfully you can try accessing the WSO2 ESB Administration Console through https://localhost:9444/esb
1. WSO2 Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) Version 1.7
2. WebSphere Application Server Version 6.1
Downloading and Installing WebSphere Application Server
Download the WebSphere Application Server Version 6.1 and execute the setup to install it on your local machine.
Creating a profile
Before deploying the WSO2 ESB application we need to create a profile through the Profile Management Tool. This is described in detail in the tutorial Running WSO2 WSAS on an IBM WebSphere Application Server under the heading Creating an IBM WebSphere Application Server Profile by Upul Godage.
NOTE: Make sure you set the HTTPS transport port to 9444.
Starting the Websphere Application server
Once you have created the profile start the application server through Start -> All Programs -> IBM WebSphere -> Application Server V6.1 -> Profiles -> [your_profile] -> Start the server.
Login into the Administrative Console
When the server is started successfully access the Administrative Console through Start -> All Programs -> IBM WebSphere -> Application Server V6.1 -> Profiles -> [your_profile] -> Administrative Console.
Once clicked it would open up a web browser. Enter the username and password that we gave in the Administrative Security step when creating the profile and then click on the button Log in.
E.g.:-
User ID: admin
Password: admin
Downloading WSO2 ESB and creating a war file
Download WSO2 ESB version 1.7 from the WSO2 site and extract it to a preferred location of yours. (E.g.:- C:\wso2esb-1.7.1). From this point onwards I will be referring to this folder as ESB_HOME. Before creating the war file you need to change some of the configuration files. Let us look at these files one by one.
1. axis2.xml
a) Open the axis2.xml located at ESB_HOME/webapp/WEB-INF/classes/conf
b) Search all the places where it specifies the jks file locations and replace them with the absolute paths.
E.g.:-
Change
<Location>webapp/WEB-INF/classes/conf/identity.jks</Location>
to
<Location>C:/wso2esb-1.7.1/webapp/WEB-INF/classes/conf/identity.jks</Location>
2. web.xml
a) Open the web.xml file located at ESB_HOME/webapp/WEB-INF
b) Specify the absolute location of the ESB_HOME
E.g.:-
Replace
<init-param>
<param-name>esb.home</param-name>
<param-value>.</param-value>
</init-param>
with
<init-param>
<param-name>esb.home</param-name>
<param-value>C:/wso2esb-1.7.1</param-value>
</init-param>
Next we have to start up a Derby server for WSO2 ESB to connect to. Since we have an issue in getting the Derby server which resides in Websphere up and running, we will be starting an external Derby server.
To do this, download the latest Derby binary and extract to a preferred location of yours. For testing purposes we will be using version 10.3.1.4. Then go to the folder DERBY_HOME/bin folder and type the following command.
NetworkServerControl start -p 1528 To direct the WSO2 ESB to connect to the external Derby server you need to set the StartEmbeddedDerby property to 'false' of the ESB_HOME/webapp/WEB-INF/classes/conf/server.xml file
<StartEmbeddedDerby>false</StartEmbeddedDerby>You are all set to create the war file. Now go to the folder 'webapp' of your ESB_HOME and open a command window.
Type the following command and it will create esb.war file in ESB_HOME/webapp folder
jar -cvf esb.war *Installing the WSO2 ESB appliacation on IBM Websphere
Follow the step described below to successfully install the WSO2 ESB application.
1. Once logged in to the Administrative Console, click on Applications -> Install New Application
2. Under Preparing for the application installation browse for the esb.war file that you created above. Specify the context root as esb. If you need to see the steps when installing the WSO2 ESB Application, select the combo box option Show me all installation options and parameters and click Next.
3. From the page loaded to generate default bindings and mappings click on Next without changing any options
4. Click on Continue given under Application Security Warnings page
5. When Install New Application -> Select installation options is loaded specify a name that you prefer as the Application name. Tick the check box Enable class reloading and specify the Reload interval in seconds as 60 seconds and then click on Next
6. Under Install New Application -> Map modules to servers do not select any options and just click on the button Next
7. When the page Install New Application -> Provide JSP reloading options for Web modules loads click on the button Next without selecting anything
8. Next do not select any options given under the page Install New Application -> Map shared libraries and simply click on Next
9. When the page Install New Application -> Initialize parameters for servlets is loaded check whether the specified parameters are correct and click on Next
10. Click on Next without selecting any options when Install New Application -> Map virtual hosts for Web modules page is loaded
11. Verify whether the value given as the context root is correct in the page Install New Application -> Map context roots for Web modules and click on Next
12. When the Install New Application -> Summary page loads, go through the values which you have specified and if they are correct click on Finish
Once you click on Continue you will get a message as follows. Therefore click on Save and the application will be installed successfully.
Configuring the WSO2 ESB Application
Go to Applications -> Enterprise Applications and click on the esb entry from the list of applications available.
Then refer the section Configuring IBM WebSphere Application Server in the tutorial Running WSO2 WSAS on an IBM WebSphere Application Server by Upul Godage.
Follow the steps specified and once you are done with setting all the properties select the esb application from the Enterprise Applications list and click on Start. This will start the WSO2 ESB server. If the server starts successfully you can try accessing the WSO2 ESB Administration Console through https://localhost:9444/esb
Monday, October 6, 2008
Starting the Derby Network Server on a new port
I was testing WSO2 ESB on IBM Websphere and I could not get the Derby server inside Websphere running and therefore wanted to start a new Derby server outside Websphere. I was struggling to get this working till I came across a link which was specified by one of my colleges in one of the WSO2 ESB forum posts. In that article it clearly specifies how you can start a new Derby server on a new port.
NetworkServerControl start -p 1528
Generally when you start up WSO2 ESB it would start a Derby database which is embedded inside WSO2 ESB. Therefore if you want the ESB instance to listen to the new Derby server which you started on port 1528 then all you have to do is set the following property to false of the ESB_HOME/webapp/WEB-INF/classes/conf/server.xml file.
<StartEmbeddedDerby>false</StartEmbeddedDerby>
NetworkServerControl start -p 1528
Generally when you start up WSO2 ESB it would start a Derby database which is embedded inside WSO2 ESB. Therefore if you want the ESB instance to listen to the new Derby server which you started on port 1528 then all you have to do is set the following property to false of the ESB_HOME/webapp/WEB-INF/classes/conf/server.xml file.
<StartEmbeddedDerby>false</StartEmbeddedDerby>
Friday, October 3, 2008
How to disable chunking/keep-alive when using Synapse
How do you disable chunking/keep-alive? Many users have asked this question through the Synapse/WSO2 ESB mailing lists several times. This is possible through the Property mediator.
Generally chunking is enabled by default. If you need to disable chunking/keep-alive all you have to do is set the property "FORCE_HTTP_1.0" to "TRUE" in the scope axis2 using Property Mediator
Generally chunking is enabled by default. If you need to disable chunking/keep-alive all you have to do is set the property "FORCE_HTTP_1.0" to "TRUE" in the scope axis2 using Property Mediator
Thursday, October 2, 2008
How to enable JMX monitoring support on Synapse
How do you enable JMX monitoring support on Synapse? This is a question that may arise in someone who would try out Synapse. In order to do this you will have to add the following line to the synapse.sh file
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote
Once this line is added you just need to start the Synapse server. When the Synapse server is started, open a new terminal window and type the command 'jconsole' and then you will be given the Monitoring & Management Console along with the available servers to connect
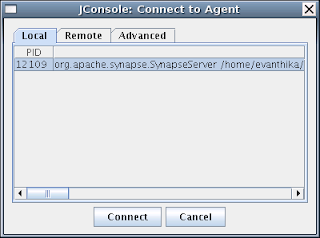
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote
Once this line is added you just need to start the Synapse server. When the Synapse server is started, open a new terminal window and type the command 'jconsole' and then you will be given the Monitoring & Management Console along with the available servers to connect

Friday, September 26, 2008
How to get a thread dump of WSO2 Servers
I will explain in terms of the product WSO2 ESB.
When WSO2 ESB server is running, find the process ID by using the following command
ps -ef | grep wso2esb
Once you find the process ID, use the following command and then you will get a thread dump on the WSO2 ESB console
kill -3 [ProcessID_of_WSO2ESB]
Also, you can get the thread dump to a text file by giving a command as follows
jstack $PID > thread_dump.txt
When WSO2 ESB server is running, find the process ID by using the following command
ps -ef | grep wso2esb
Once you find the process ID, use the following command and then you will get a thread dump on the WSO2 ESB console
kill -3 [ProcessID_of_WSO2ESB]
Also, you can get the thread dump to a text file by giving a command as follows
jstack $PID > thread_dump.txt
Wednesday, September 24, 2008
Setting up WSO2 ESB in a clustered environment
I will briefly describe how one can easily set up WSO2 ESB in a clustered environment.
Prerequisites
Download the latest version of WSO2 ESB and extract to a folder of your choice. (I will refer to the two WSO2 ESB instances as cluster1 and cluster2)
NOTE: I will be having both the WSO2 ESB instances on my local machine.
Step 1
Out of the two WSO2 ESB instances, select one and edit the default ports. (cluster2)
a) axis2.xml ($ESB_HOME/webapp/WEB-INF/classes/conf)
- To enable clustering uncomment the following of both ESB instances
<parameter name="AvoidInitiation">false</parameter>
<parameter name="domain">wso2esb.domain</parameter>
...
...
</cluster>
- Change the HTTP and HTTPS ports specified in the axis2.xml of cluster2 (E.g.:- HTTP - 8281 , HTTPS - 8244)
b) tomcat.properties of cluster2 should also be changed as follows ($ESB_HOME/tomcat/config)
Change the Admin console port given in the tomcat.properties file (E.g.:- 9443)
Step 2
Edit the ./wso2esb.sh file of both the instances (cluster1 and cluster2) and add the following
-Daxis2.local.ip.address=<Your_IP>
Now you are all ready to start the two WSO2 ESB instances in the clustered environment
Prerequisites
Download the latest version of WSO2 ESB and extract to a folder of your choice. (I will refer to the two WSO2 ESB instances as cluster1 and cluster2)
NOTE: I will be having both the WSO2 ESB instances on my local machine.
Step 1
Out of the two WSO2 ESB instances, select one and edit the default ports. (cluster2)
a) axis2.xml ($ESB_HOME/webapp/WEB-INF/classes/conf)
- To enable clustering uncomment the following of both ESB instances
<parameter name="AvoidInitiation">false</parameter>
<parameter name="domain">wso2esb.domain</parameter>
...
...
</cluster>
- Change the HTTP and HTTPS ports specified in the axis2.xml of cluster2 (E.g.:- HTTP - 8281 , HTTPS - 8244)
b) tomcat.properties of cluster2 should also be changed as follows ($ESB_HOME/tomcat/config)
Change the Admin console port given in the tomcat.properties file (E.g.:- 9443)
Step 2
Edit the ./wso2esb.sh file of both the instances (cluster1 and cluster2) and add the following
-Daxis2.local.ip.address=<Your_IP>
Now you are all ready to start the two WSO2 ESB instances in the clustered environment
Thursday, September 18, 2008
Reliable message exchange with WSO2 ESB - Invoking WS-RM Service using nonWS-RM one-way client
Invoking a WS-RM enabled service using a one-way client where WS-RM is not enabled
Reliable messaging allows messages to be delivered reliably between applications in the presence of system, or network failures. I will breifly describe how reliable messaging is made possible with WSO2 ESB along with some samples. Step by step information will be provided on how to configure WSO2 ESB to handle the exchanging of messages between WS-Reliable Messaging (WS-RM) enabled services and clients.
To start off with, you will need to download and install WSO2 ESB on your machine. (Refer https://wso2.org/project/esb/java/1.7.1/docs/installationguide.html on how to download and install WSO2 ESB). From this point onwards the location where WSO2 ESB is installed will be refered to as ESB_HOME.
Step 1 - Creating and deploying a WS-RM enabled service.
The implementation class should be created as follows.
package org.wso2.esb.services;
public class RMService {
public void Ping(String x){
System.out.println("Received Ping request");
}
}
Then create a services.xml file as follows
<service name="RMService">
<description>This service is created to add two numbers.</description>
<parameter name="ServiceClass" locked="false">org.wso2.esb.services.RMService</parameter>
<messageReceivers>
<messageReceiver mep="http://www.w3.org/2006/01/wsdl/in-only" class="org.apache.axis2.rpc.receivers.RPCInOnlyMessageReceiver"/>
<messageReceiver mep="http://www.w3.org/2006/01/wsdl/in-out" class="org.apache.axis2.rpc.receivers.RPCMessageReceiver"/>
</messageReceivers>
<module ref="Mercury"/>
</service>
Place the above services.xml file in a directory named META-INF. Compile the RMService class and get the compiled class, bundle it with the META-INF file and create an .aar file. For testing purposes we will be using the SimpleAxisServer which comes with the WSO2 ESB package so deploy the services. Therefore drop the created archive file in ESB_HOME/samples/axis2Server/repository/services. (To check if the service has been deployed successfully access http://localhost:9000/soap)
Step 2 - Creating the WSO2 ESB Configuration
Start the WSO2 ESB server located at ESB_HOME/bin and access the WSO2 ESB Admin console through https://localhost:9444/esb/
Inorder for the non-WS-RM client to communicate with the WS-RM enabled service the folling configuration should be used. Log in to the WSO2 ESB admin console (username - admin, password - admin) and create the following configuration.
<definitions xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse">
<proxy name="RMProxy" transports="http" startOnLoad="true" statistics="enable">
<target>
<inSequence>
<RMSequence single="true" version="1.0"/>
<send>
<endpoint>
<address uri="http://localhost:9000/soap/RMService">
<enableAddressing/>
<enableRM/>
</address>
</endpoint>
</send>
</inSequence>
<outSequence>
<send/>
</outSequence>
</target>
<enableRM/>
</proxy>
</definitions>
Step 3 - Generating Stubs
Inorder for the client to successfully execute we need to generate stubs. This can easily be done through WSO2 WSAS. (Refer http://charithaka.blogspot.com/2008/02/securing-axis2wsas-web-services-with.html Step 3). For ease of use I will be providing a generated jar file which works with the below client code. You can download it from here
Make sure to add jars in ESB_HOME/lib and the above downloaded client stub jar to your class path in order to compile the client.
Step 4 - Create a non-WS-RM Client
The next step would be create a client to invoke the WS-RM enabled service as follows. The below client supports only SOAP11 messages. For you to try out SOAP12 messages you can use the client OneWayAnnonSOAP12Client.
public class OneWayAnnonSOAP11Client {
public static void main(String[] args)throws AxisFault {
ConfigurationContext cc = ConfigurationContextFactory.createConfigurationContextFromFileSystem("/home/rmScenario/client_repo","/home/rmScenario/client-repo/axis2.xml");
OMElement payload = createPayLoad();
ServiceClient serviceclient = new ServiceClient(cc, null);
Options opts = new Options();
opts.setTo(new EndpointReference("http://localhost:8280/soap/RMProxy"));
opts.setAction("urn:Ping");
serviceclient.setOptions(opts);
try {
serviceclient.fireAndForget(payload);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static OMElement createPayLoad(){
OMFactory fac = OMAbstractFactory.getOMFactory();
OMNamespace omNs = fac.createOMNamespace("http://service.esb.wso2.org", "ns");
OMElement method = fac.createOMElement("Ping", omNs);
OMElement value = fac.createOMElement("ping", omNs);
value.addChild(fac.createOMText(method, "pong"));
method.addChild(value);
return method;
}
}
You can access the entire client code from here.
Before you execute the client, make sure you have copied the Mercury.mar (make sure that the mar file is inside a folder named 'module') and axis2.xml to the specified locations above.
Step 5 - Starting the Simple Axis2 Server
Go to the ESB_HOME/samples/axis2Server and start the simple axis2server
E.g.:- sh ./axis2Server.sh
Step 6 - Executing the client
Now you are all set to execute the client. To see whether the messages are being sent properly you can send them through TCPMon.
Reliable messaging allows messages to be delivered reliably between applications in the presence of system, or network failures. I will breifly describe how reliable messaging is made possible with WSO2 ESB along with some samples. Step by step information will be provided on how to configure WSO2 ESB to handle the exchanging of messages between WS-Reliable Messaging (WS-RM) enabled services and clients.
To start off with, you will need to download and install WSO2 ESB on your machine. (Refer https://wso2.org/project/esb/java/1.7.1/docs/installationguide.html on how to download and install WSO2 ESB). From this point onwards the location where WSO2 ESB is installed will be refered to as ESB_HOME.
Step 1 - Creating and deploying a WS-RM enabled service.
The implementation class should be created as follows.
package org.wso2.esb.services;
public class RMService {
public void Ping(String x){
System.out.println("Received Ping request");
}
}
Then create a services.xml file as follows
<service name="RMService">
<description>This service is created to add two numbers.</description>
<parameter name="ServiceClass" locked="false">org.wso2.esb.services.RMService</parameter>
<messageReceivers>
<messageReceiver mep="http://www.w3.org/2006/01/wsdl/in-only" class="org.apache.axis2.rpc.receivers.RPCInOnlyMessageReceiver"/>
<messageReceiver mep="http://www.w3.org/2006/01/wsdl/in-out" class="org.apache.axis2.rpc.receivers.RPCMessageReceiver"/>
</messageReceivers>
<module ref="Mercury"/>
</service>
Place the above services.xml file in a directory named META-INF. Compile the RMService class and get the compiled class, bundle it with the META-INF file and create an .aar file. For testing purposes we will be using the SimpleAxisServer which comes with the WSO2 ESB package so deploy the services. Therefore drop the created archive file in ESB_HOME/samples/axis2Server/repository/services. (To check if the service has been deployed successfully access http://localhost:9000/soap)
Step 2 - Creating the WSO2 ESB Configuration
Start the WSO2 ESB server located at ESB_HOME/bin and access the WSO2 ESB Admin console through https://localhost:9444/esb/
Inorder for the non-WS-RM client to communicate with the WS-RM enabled service the folling configuration should be used. Log in to the WSO2 ESB admin console (username - admin, password - admin) and create the following configuration.
<definitions xmlns="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse">
<proxy name="RMProxy" transports="http" startOnLoad="true" statistics="enable">
<target>
<inSequence>
<RMSequence single="true" version="1.0"/>
<send>
<endpoint>
<address uri="http://localhost:9000/soap/RMService">
<enableAddressing/>
<enableRM/>
</address>
</endpoint>
</send>
</inSequence>
<outSequence>
<send/>
</outSequence>
</target>
<enableRM/>
</proxy>
</definitions>
Step 3 - Generating Stubs
Inorder for the client to successfully execute we need to generate stubs. This can easily be done through WSO2 WSAS. (Refer http://charithaka.blogspot.com/2008/02/securing-axis2wsas-web-services-with.html Step 3). For ease of use I will be providing a generated jar file which works with the below client code. You can download it from here
Make sure to add jars in ESB_HOME/lib and the above downloaded client stub jar to your class path in order to compile the client.
Step 4 - Create a non-WS-RM Client
The next step would be create a client to invoke the WS-RM enabled service as follows. The below client supports only SOAP11 messages. For you to try out SOAP12 messages you can use the client OneWayAnnonSOAP12Client.
public class OneWayAnnonSOAP11Client {
public static void main(String[] args)throws AxisFault {
ConfigurationContext cc = ConfigurationContextFactory.createConfigurationContextFromFileSystem("/home/rmScenario/client_repo","/home/rmScenario/client-repo/axis2.xml");
OMElement payload = createPayLoad();
ServiceClient serviceclient = new ServiceClient(cc, null);
Options opts = new Options();
opts.setTo(new EndpointReference("http://localhost:8280/soap/RMProxy"));
opts.setAction("urn:Ping");
serviceclient.setOptions(opts);
try {
serviceclient.fireAndForget(payload);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static OMElement createPayLoad(){
OMFactory fac = OMAbstractFactory.getOMFactory();
OMNamespace omNs = fac.createOMNamespace("http://service.esb.wso2.org", "ns");
OMElement method = fac.createOMElement("Ping", omNs);
OMElement value = fac.createOMElement("ping", omNs);
value.addChild(fac.createOMText(method, "pong"));
method.addChild(value);
return method;
}
}
You can access the entire client code from here.
Before you execute the client, make sure you have copied the Mercury.mar (make sure that the mar file is inside a folder named 'module') and axis2.xml to the specified locations above.
Step 5 - Starting the Simple Axis2 Server
Go to the ESB_HOME/samples/axis2Server and start the simple axis2server
E.g.:- sh ./axis2Server.sh
Step 6 - Executing the client
Now you are all set to execute the client. To see whether the messages are being sent properly you can send them through TCPMon.
Wednesday, July 9, 2008
How to deploy WSO2 ESB on Apache Tomcat
WSO2 ESB can be deployed on differnt application servers such as IBM WebSphere, BEA WebLogic Server, JBoss and Apache Tomcat. I will be describing how one can easily deploy WSO2 ESB on Apache Tomcat. A similar article has been written on how to deploy WSO2 ESB on WebLogic by Asankha Perera - Running the WSO2 Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) on the WebLogic Application Server.
Step 1 - Downloading and installing Apache Tomcat
You can download the latest version of Apache Tomcat from here (I will be using Apache Tomcat 5.5.26 to demonstrate this scenario).
Extract the downloaded distribution to a specific location and define the environment variables properly.
E.g.: -
export CATALINA_HOME=/opt/installations/tomcat/apache-
tomcat-5.5.26
export PATH=$PATH:$CATALINA_HOME/bin
Next you will need to enable HTTPS on Apache Tomcat since WSO2 ESB runs over HTTPS. To do this, access the server.xml file located at $CATALINA_HOME/conf and uncomment the following.
<Connector port="8443" maxHttpHeaderSize="8192"
maxThreads="150" minSpareThreads="25" maxSpareThreads="75"
enableLookups="false" disableUploadTimeout="true"
acceptCount="100" scheme="https" secure="true"
clientAuth="false" sslProtocol="TLS"/>
Then you will need to provide the keystore file location along with it's password as below.
<Connector port="8443" maxHttpHeader
maxThreads="150" minSpareThreads="25" maxSpareThreads="75"
enableLookups="false" disableUploadTimeout="true"
acceptCount="100" scheme="https" secure="true"
clientAuth="false" sslProtocol="TLS"
keystore="/opt/wso2esb-1.7/webapp/WEB-INF/classes
/conf/identity.jks"
keypass="password">
Step 2 - Starting the Apache Tomcat Server
Now you can start the Apache Tomcat server by giving the following command.
sh ./catalina.sh run
Step 3 - Downloading and installing WSO2 ESB
Download the latest WSO2 ESB distribution from here and extract to a specific location. (E.g.:- /opt/wso2esb-1.7)
Step 4 - Changing necessary files of the WSO2 ESB distribution
In order for the deployement to be successful you will need to change some files of the WSO2 ESB distribution.
a) Editing the web.xml
<servlet>
<servlet-name>ESBStartUpServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.wso2.esb.transport.tomcat.
StartUpServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>esb.home</param-name>
<param-value>/opt/wso2esb-1.7</param-value>
</init-param>
b) Editing the axis2.xml
Next you will need to change the paths of the keystore and truststore files specified in the axis2.xml as below specifying the absolute paths.
<parameter name="keystore" locked="false">
<KeyStore>
<Location>/opt/wso2esb-1.7/webapp/WEB-INF/
classes/conf/identity.jks</Location>
<Type>JKS</Type>
<Password>password</Password>
<KeyPassword>password</KeyPassword>
</KeyStore>
</parameter>
<parameter name="truststore" locked="false">
<TrustStore>
<Location>/opt/wso2esb-1.7/webapp/WEB-INF
/classes/conf/trust.jks</Location>
<Type>JKS</Type>
<Password>password</Password>
</TrustStore>
</parameter>
Now all the required files are edited and you can create a .war file with all the required files of WSO2 ESB.
Step 5 - Creating the WSO2 ESB .war file
Navigate to the folder /opt/wso2esb-1.7/webapp and type the command.
jar -cvf esb.war *
It would create a war file inside the /opt/wso2esb-1.7/webapp folder.
Step 6 - Deploying the esb.war on Apache Tomcat
Now navigate to $CATALINA_HOME/webapps folder and drop the esb.war file which you created. If everything goes well the WSO2 ESB server should start successfully and you should see something like the following on the console which you started the Apache Tomcat server.
2008-07-09 15:09:02,030 ......INFO ServerManager Ready for processing
2008-07-09 15:09:03,654 ......INFO ServiceBusManager [ESB] Start request completed
Step 7 - Login to the WSO2 ESB Administration Console
Now you should be able to login to the WSO2 ESB Administration Console as, https://localhost:8443/esb
Step 1 - Downloading and installing Apache Tomcat
You can download the latest version of Apache Tomcat from here (I will be using Apache Tomcat 5.5.26 to demonstrate this scenario).
Extract the downloaded distribution to a specific location and define the environment variables properly.
E.g.: -
export CATALINA_HOME=/opt/installations/tomcat/apache-
tomcat-5.5.26
export PATH=$PATH:$CATALINA_HOME/bin
Next you will need to enable HTTPS on Apache Tomcat since WSO2 ESB runs over HTTPS. To do this, access the server.xml file located at $CATALINA_HOME/conf and uncomment the following.
<Connector port="8443" maxHttpHeaderSize="8192"
maxThreads="150" minSpareThreads="25" maxSpareThreads="75"
enableLookups="false" disableUploadTimeout="true"
acceptCount="100" scheme="https" secure="true"
clientAuth="false" sslProtocol="TLS"/>
Then you will need to provide the keystore file location along with it's password as below.
<Connector port="8443" maxHttpHeader
maxThreads="150" minSpareThreads="25" maxSpareThreads="75"
enableLookups="false" disableUploadTimeout="true"
acceptCount="100" scheme="https" secure="true"
clientAuth="false" sslProtocol="TLS"
keystore="/opt/wso2esb-1.7/webapp/WEB-INF/classes
/conf/identity.jks"
keypass="password">
Step 2 - Starting the Apache Tomcat Server
Now you can start the Apache Tomcat server by giving the following command.
sh ./catalina.sh run
Step 3 - Downloading and installing WSO2 ESB
Download the latest WSO2 ESB distribution from here and extract to a specific location. (E.g.:- /opt/wso2esb-1.7)
Step 4 - Changing necessary files of the WSO2 ESB distribution
In order for the deployement to be successful you will need to change some files of the WSO2 ESB distribution.
a) Editing the web.xml
To begin with you will need to change the init parameter of "ESBStartUpServlet" of the web.xml which is located at /opt/wso2esb-1.7/webapp/WEB-INF as below.
<servlet>
<servlet-name>ESBStartUpServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.wso2.esb.transport.tomcat.
StartUpServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>esb.home</param-name>
<param-value>/opt/wso2esb-1.7</param-value>
</init-param>
b) Editing the axis2.xml
Next you will need to change the paths of the keystore and truststore files specified in the axis2.xml as below specifying the absolute paths.
<parameter name="keystore" locked="false">
<KeyStore>
<Location>/opt/wso2esb-1.7/webapp/WEB-INF/
classes/conf/identity.jks</Location>
<Type>JKS</Type>
<Password>password</Password>
<KeyPassword>password</KeyPassword>
</KeyStore>
</parameter>
<parameter name="truststore" locked="false">
<TrustStore>
<Location>/opt/wso2esb-1.7/webapp/WEB-INF
/classes/conf/trust.jks</Location>
<Type>JKS</Type>
<Password>password</Password>
</TrustStore>
</parameter>
Now all the required files are edited and you can create a .war file with all the required files of WSO2 ESB.
Step 5 - Creating the WSO2 ESB .war file
Navigate to the folder /opt/wso2esb-1.7/webapp and type the command.
jar -cvf esb.war *
It would create a war file inside the /opt/wso2esb-1.7/webapp folder.
Step 6 - Deploying the esb.war on Apache Tomcat
Now navigate to $CATALINA_HOME/webapps folder and drop the esb.war file which you created. If everything goes well the WSO2 ESB server should start successfully and you should see something like the following on the console which you started the Apache Tomcat server.
2008-07-09 15:09:02,030 ......INFO ServerManager Ready for processing
2008-07-09 15:09:03,654 ......INFO ServiceBusManager [ESB] Start request completed
Step 7 - Login to the WSO2 ESB Administration Console
Now you should be able to login to the WSO2 ESB Administration Console as, https://localhost:8443/esb
Monday, June 30, 2008
Database interactions in mediation using DBLookup and DBReport mediators with MySQL
MySQL is known to be the world's most popular open source database due to its fast performance. It is a known fact that a many individuals as well as a lot of world's largest organizations such as Yahoo, Google, Nokia and YouTube use MySQL as their database to save time and money. WS02 ESB has a wide variety of mediators that enables us to connect, manage and transform service interactions between Web services. The DBLookup and DBReport mediators allows you to read data from a database and also to write to a database. Generally we use Apache Derby as the database in our samples but we can use MySQL as well. Let us see how we can use these mediators to look up and report to a MySQL database. Step 1 - Setting up the MySQL database
You will need to install MySQL server on your machine. Once you have installed MySQL, log into the database using the command
mysql -u <username> -p
E.g.:- mysql -u root -p
Create a database using the following command.
create database esb;
Select the newly created database as follows
CREATE table company(name varchar(10), id varchar(10), price double);
Now create a table using the following command on the newly created database
INSERT into company values ('IBM','c1',0.0);
INSERT into company values ('SUN','c2',0.0);
INSERT into company values ('MSFT','c3',0.0);
Step 2 - Installing WSO2 ESB
a) Downloading the binary distribution
You will need to install WSO2 ESB on your machine. You can download the latest ESB binary distribution from here.
b) Deploying the service
d) Starting the WSO2 ESB server
Step 3 - Create configuration
The following configuration sends a request to a service and receives a response and then the database is updated from those retrieved response values. Create the following configuration using the WS02 ESB admin console.
NOTE: When using MySQL as the database make sure that you set the following property in the configurationYou will need to install MySQL server on your machine. Once you have installed MySQL, log into the database using the command
mysql -u <username> -p
E.g.:- mysql -u root -p
Create a database using the following command.
create database esb;
Select the newly created database as follows
CREATE table company(name varchar(10), id varchar(10), price double);
Now create a table using the following command on the newly created database
INSERT into company values ('IBM','c1',0.0);
INSERT into company values ('SUN','c2',0.0);
INSERT into company values ('MSFT','c3',0.0);
Step 2 - Installing WSO2 ESB
a) Downloading the binary distribution
You will need to install WSO2 ESB on your machine. You can download the latest ESB binary distribution from here.
b) Deploying the service
Extract the distribution and navigate to the ESB_HOME/samples/axis2Server folder and start the Axis2 Server. To deploy the SimpleStockQuoteService go to ESB_HOME/samples/axis2Server/src/SimpleStockQuoteService and type 'ant' and it will build the particular service. You can verify whether the service has been deployed successfully by accessing the URL http://localhost:9000/soap/
c) Starting the Simple Axis2 Server
To start the simple axis server navigate to ESB_HOME/samples/axis2Server and run ./axis2Server.sh. Then it would start the axis2 server on port 9000
c) Starting the Simple Axis2 Server
To start the simple axis server navigate to ESB_HOME/samples/axis2Server and run ./axis2Server.sh. Then it would start the axis2 server on port 9000
d) Starting the WSO2 ESB server
To start the WSO2 ESB server go to ESB_HOME/bin and run ./wso2-esb.sh. Once the WSO2 ESB server is started you will be able to access the WSO2 ESB admin console using https://localhost:9444/esb
Step 3 - Create configuration
The following configuration sends a request to a service and receives a response and then the database is updated from those retrieved response values. Create the following configuration using the WS02 ESB admin console.
<syn:definitions xmlns:syn="http://ws.apache.org/ns/synapse">
<syn:sequence name="sample_sequence2">
<syn:in>
<syn:send>
<syn:endpoint>
<syn:address uri="http://localhost:9000/soap/SimpleStockQuoteService"/>
</syn:endpoint>
</syn:send>
</syn:in>
<syn:out>
<syn:log level="custom">
<syn:property name="text" value="** Reporting to the Database **"/>
</syn:log>
<syn:dbreport>
<syn:connection>
<syn:pool>
<syn:driver>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</syn:driver>
<syn:property name="autocommit" value="false"/>
<syn:password>admin</syn:password>
<syn:user>root</syn:user>
<syn:url>jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/esb</syn:url>
</syn:pool>
</syn:connection>
<syn:statement>
<syn:sql><update company set price=? where name =?></syn:sql>
<syn:parameter xmlns:m0="http://services.samples/xsd" xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" expression="//m0:return/m0:last/child::text()" type="DOUBLE"/>
<syn:parameter xmlns:m0="http://services.samples/xsd" xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" expression="//m0:return/m0:symbol/child::text()" type="VARCHAR"/>
</syn:statement>
</syn:dbreport>
<syn:log level="custom">
<syn:property name="text" value="** Looking up from the Database **"/>
</syn:log>
<syn:dblookup>
<syn:connection>
<syn:pool>
<syn:driver>com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</syn:driver>
<syn:password>admin</syn:password>
<syn:user>root</syn:user>
<syn:url>jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/esb</syn:url>
</syn:pool>
</syn:connection>
<syn:statement>
<syn:sql><select * from company where name =?></syn:sql>
<syn:parameter xmlns:m0="http://services.samples/xsd" xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" expression="//m0:return/m0:symbol/child::text()" type="VARCHAR"/>
<syn:result name="stock_price" column="price"/>
</syn:statement>
</syn:dblookup>
<syn:log level="custom">
<syn:property xmlns:ns1="http://org.apache.synapse/xsd" xmlns:soapenv="http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/" name="text" expression="fn:concat('Stock price - ',get-property('stock_price'))"/>
</syn:log>
<syn:send/>
</syn:out>
</syn:sequence>
</syn:definitions>
<syn:property name="autocommit" value="false"/>Step 4 - Invoking the client
Once the configuration is created you should be able to invoke the stockquote client using the following command.
ant stockquote -Daddurl=http://localhost:9000/soap/SimpleStockQuoteService -Dtrpurl=http://localhost:8280/ -Dsymbol=IBM
If the client executes successfully you should see the following on the WSO2 ESB console
DEBUG LogMediator Start : Log mediator
INFO LogMediator text = ** Reporting to the Database **
DEBUG LogMediator End : Log mediator
....
DEBUG DBReportMediator Successfully prepared statement : update company set price=? where name =? against DataSource : jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/esb
DEBUG DBReportMediator Inserted 1 row/s using statement : update company set price=? where name =?
....
DEBUG LogMediator Start : Log mediator
INFO LogMediator text = ** Looking up from the Database **
DEBUG LogMediator End : Log mediator
....
DEBUG DBLookupMediator Successfully prepared statement : select * from company where name =? against DataSource : jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/esb
DEBUG DBLookupMediator End : DBLookup mediator
DEBUG LogMediator Start : Log mediator
INFO LogMediator text = Stock price - 147.286209770313
DEBUG LogMediator End : Log mediator
Finally you can check if the company table has been updated with the new stock value by a simple query.
Monday, February 4, 2008
Using WAST for ESB/WSAS performance testing - not a good choice
Last November I blogged about WAST and how this tool can be used for Web Application Stress Testing. In that I made a statement saying that it would be great if we can use this tool for our own products such as ESB and WSAS. During the two week vacation I got due to my illness, I thought I should do some research to see if we can actually use this tool for ESB.
So I first started the ESB server along with the axis2Server and then started recording. Once the recording started a Firefox browser window opened asking to enter the web address. Therefore I entered the proper URL and started doing some operations in the Administration Console. (E.g.:- Logged in, Click on Proxy Services link, etc). Then I stopped the recording to see if it has been properly done and to my surprise nothing was recorded. I was quite confused. I was pretty sure that I did everything properly but then again I have not read the manual properly. It clearly states that this can be used with Internet Explorer only. So this was the first reason for me to give up on this. Then I tried to record on IE but again failed since WAST does not support HTTPS. If you want to test a secured site like ESB you will manually have to go and change the URL, which was quite annoying.
So due to these drawbacks I think that we should focus more on some other tools which we can easily use for stress testing without having to put so much effort like we have to when using WAST. On the other hand if we spend a little bit of time on this particular tool we might be able to get some use for our products. I'm sure we can but it requires a little bit of effort. So while checking for other alternatives it is advisable that we do more research on WAST as well.
Refer http://www.microsoft.com/technet/archive/itsolutions/intranet/downloads/webstres.mspx?mfr=true for it's limitations.
So I first started the ESB server along with the axis2Server and then started recording. Once the recording started a Firefox browser window opened asking to enter the web address. Therefore I entered the proper URL and started doing some operations in the Administration Console. (E.g.:- Logged in, Click on Proxy Services link, etc). Then I stopped the recording to see if it has been properly done and to my surprise nothing was recorded. I was quite confused. I was pretty sure that I did everything properly but then again I have not read the manual properly. It clearly states that this can be used with Internet Explorer only. So this was the first reason for me to give up on this. Then I tried to record on IE but again failed since WAST does not support HTTPS. If you want to test a secured site like ESB you will manually have to go and change the URL, which was quite annoying.
So due to these drawbacks I think that we should focus more on some other tools which we can easily use for stress testing without having to put so much effort like we have to when using WAST. On the other hand if we spend a little bit of time on this particular tool we might be able to get some use for our products. I'm sure we can but it requires a little bit of effort. So while checking for other alternatives it is advisable that we do more research on WAST as well.
Refer http://www.microsoft.com/technet/archive/itsolutions/intranet/downloads/webstres.mspx?mfr=true for it's limitations.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)